CIL - Common Intermediate Language
CIL (Common Intermediate Langue) is a baytecode, a portable .NET platform language that compiles sources written in high-level languages. Its operation is stack-based and executed by a virtual machine.
It is also called IL or MSIL (MicroSoft Intermediate Language), which was its original name before the standardization of the CLI (Common Language Infrastructure) of which it is a part and with which it should not be confused.
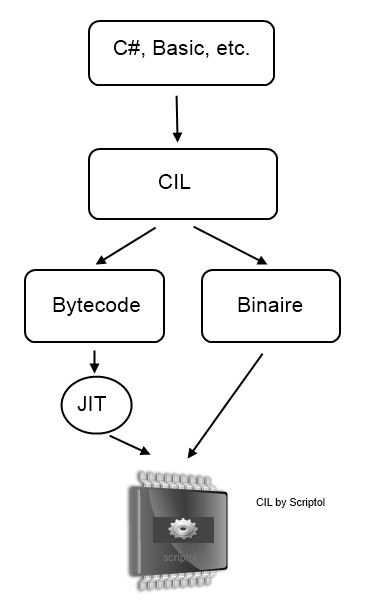
High-level source code (C #, Basic, or another language) is compiled in CIL and stored in an assembly (or build).
The assembly follows the PE (Portable Executable) format, which is also a DLL and .exe format, and includes a manifest file containing the assembly's medadata, which is the code interface with other software components that use it.
This code is compiled into bytecode for JIT interpretation, or binary for direct execution by the processor.
The CIL language can perform arithmetic, logical operations and has control structures (loops, if, etc.), performs calls to functions and methods, stack management, loading and backing up data, converting types (number to string...), supports exceptions and competition.
Minimum Hello program in CIL build language
.assembly Hello {}
.method public static void Main() cil managed
{
.entrypoint
.maxstack 1
ldstr "Salut le Monde!"
call void [mscorlib]System.Console::WriteLine(string)
ret
}
CIL Bytecode Example
assemblage bytecode rôle ldarga argNum FE 0A récupère l'adresse donnée en argument brtrue 2D branchement si résultat vaut vrai break 01 sortie de boucle
Reference: CIL is section 3 of the ECMA-335 standard that defines the .NET infrastructure.
Toolbox
- ILdasm is Microsoft's tool for parsing CIL code to make it human readable.
- JSIL is a tool for converting bytecode CIL to JavaScript and thereby promoting .NET applications in a browser. Several games have already been ported.
- Bridge.net is another similar but less comprehensive tool than JSIL.
See also LLVM, an even more portable alternative that can also produce JavaScript from different languages, and the explainable difference between bitcode and bytecode .