JSON, for exchanging objects between different languages
JSON (JavaScript Object Notification) - data format for exchange between the browser and the server. Its syntax is similar to that of an associative table in JavaScript. In fact, the format established in 2002 was based on a subset of the ECMA-252 language specification.
Starting with PHP 5.2, the JSON extension is part of the default PHP installation. It provides json_decode and json_encode functions that convert a string to an object or string object, which allows you to save the object to a file or pass it to a JavaScript application.
All modern browsers recognize a JSON object that transforms the object or displays it as a tree line.
JSON has even become a data type in PostgreSQL and MySQL (5.5.7). For these free Oracle competitors, JSON content can be the same data type as INTEGER or TEXT. New commands are added to use it. You can also express the result of the request in JSON.
The JSON format recognizes the same data types as JavaScript:
- Number, String, Boolean, and null are primitives that can be assigned to a key that should be a string.
- Array is a list of value keys enclosed in square brackets.
- An object is a list of value keys placed between parentheses.
How to use JSON in JavaScript
We read the JSON file on the server using a parser. They exist for the most common programming languages.
On a web page, simply provide the contents of the file as an argument to the eval () function to return an array or object that can be used directly by JavaScript.
var x = eval('(' + xhr.responseText + ')'); For example, content assigned to the responseText attribute of an XMLHttpRequest object when queried in Ajax can become an object in the program.
Before assigning an object to JavaScript with eval, it is recommended that you clear the content with a regular expression to avoid possible malicious code injection.
var doc = xhr.responseText;
var obj = !(/[^,:{}\[\]0-9.\-+Eaeflnr-u \n\r\t]/.
test( doc.replace(/"(\\.|[^"\\])*"/g, ''))) && eval('(' + doc + ')');This code is given in RFC 4627.
Since there are JSON parsers for all server-side languages, you can exchange objects between the JavaScript application and the backend in this way, for example, if it is a PHP script:
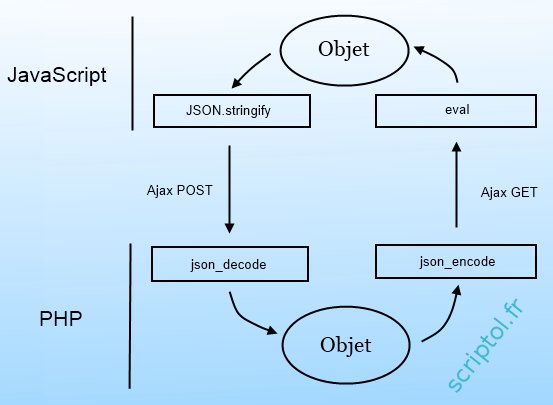
Now we have to replace eval with JSON.parse, as all browsers now support this.
JSON vs XML and other alternative formats
Here is an example of an object that contains a table. Numeric values are written as is, and strings are always enclosed in quotation marks .
JSON file:
{
"menu": "Fichier",
"commandes":
[
{
"title": "Nouveau",
"action":"create"
},
{
"title": "Ouvrir",
"action": "open"
},
{
"title": "Quitter",
"action": "exit"
}
]
} This file is a menu, the article below serves as a demonstration of its use.
XML equivalent:
<menu label="Fichier">
<menulist>
<command label="Nouveau" command="create" />
<command label="Ouvrir" command="open"/>
<command label="Quitter" command="exit" />
</menulist>
</menu>The XML version is easier to read, but for a computer the advantage is in JSON: easier, easier to parse, similar to a JavaScript object.
For a more detailed comparison, see JSON or XML, which format to choose?
Data validation can be done using the JSON schema. This will avoid the need to change the platform, as Uber did, on the grounds that the data received does not always have the expected format.
Other competing formats include YAML, a more complete but also more sophisticated and Protocol Buffers, built by Google for its servers. The latter fits better into languages other than JavaScript, because from the prototype describing the data (these would be the menu bars in our example), the compiler creates classes in C++ or Java to access them. But this is more suitable for static data .
References: Additional Json.org. information The site provides a link to the parser for each programming language. See also ECMA specification.