SQL, Database Management Language
SQL is suitable for managing large collections of data grouped into attribute lists. Classic company business, transactions and resources are perfectly managed by such a tool.
This is the most used language for building and using relational databases. The name was originally SEQUEL, the abbreviation "Structured English QUIry Language," and then was compensated in SQL and the full name "Structured Query Language" was assigned to it later.
The creators of the language are Donald D. Chamberlin and Raymond F. Boyce at IBM. The implementation of the System/38 was sold to IBM in 1979, while Oracle software was created by Relational Software in the same year (later this company was renamed Oracle).
In 1982, IBM implemented SQL in DB2.
SQL became the ANSI standard in 1986, ISO in 1987, but specific implementations are far from standardized.
SQL 2003 adds XML capabilities to the language.
The language knows several options that have different procedural extensions according to publishers .
- PL/SQL for Oracle.
- PS/PgSQL for PostgreSQL.
- SQL Procedural Language от IBM. It is a complete programming language.
- Transact SQL для MS SQL Server.
- Microsoft Access and VBA (Visual Basic for Applications).
Query Language Characteristics
In the linking model, queries are expressed declaratively as relationships between data categories (with the "and," "or" operators basically).
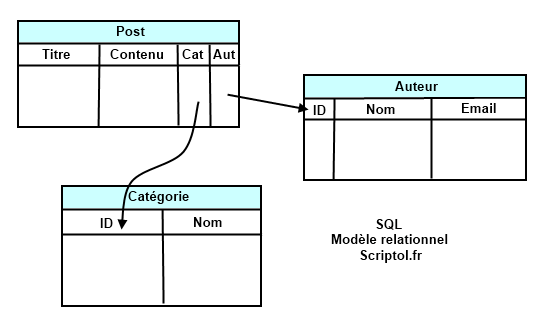
- SQL is intended mainly for interrogation.
- Extended by procedural programming languages.
- Search for data with functional queries. Tables and
- rows or rows are used.
- Data processing functions:
- Delete parts, rows.
- Insert Rows.
- Merge Tables.
- Select items.
- Updating table contents.
- Definition functions:
- Creating table, row...
- Table waiver, line...
- Control functions:
- Give the user permission to perform operations.
- Revoke user permissions.
- The comment has the form: - comment .
The main novelty of version 2003 is the ability to process XML code. In version 2006, we define exactly how to store XML and access its content with queries.
Versions 2008 and 2011 make minor changes.
It should be noted that the PostgreSQL 2013 version allows you to store JSON code in tables and access the content programmatically .
Code examples
Hello world.
CREATE TABLE message (text char(18));
INSERT INTO message (text) VALUES ('Salut, le Monde!');
SELECT text FROM message;
DROP TABLE message;
Choose items under €50.
SELECT * FROM article WHERE price < 50
The main free SQL database management software is MySQL, an implementation used by all shared hosting, SQLite, running locally or on a server, for a single database, and PostgreSQL for intensive transactions.
Documentation
French:
- SQL tutorial with PHP and MySQL. Learn how to use SQL on your website using examples. (on this site).
- PostgreSQL vs. Oracle. Comparing a free tool with the most expensive of systems.
- Manually MySQL. A reference guide to the best known SQL implementation.
English:
- Comparison. Difference between different implementations.
- SQL 92. Standard.
- SQL 2003. Standard.