WYSIWYG definition
WYSIWYG is an acronym for What You See is What You Get. What you see is what you get. This applies to text editors and presentation tools, which allow you to edit content directly in the form that will be displayed to end users, rather than by entering internal code.
For example, Dreamweaver or Komposer are WYSIWYG web page editors, unlike the first, more rustic editors, with which you had to enter HTML tag code.
However, these editors can always show the HTML source code and, if necessary, immediately enter the code in the original mode. This is rarely the case with text programs .
Example WYSIWYG text:
.fr
And HTML source code:
<a href="https://www.iqlevsha.ru" target="_top">.fr</a>
Some CMS require input of note text in coded form, such as in BBCode, others include a WYSIWYG editor.
Same text on BBCode:
[url=https://www.iqlevsha.ru].fr[/url]
Is there a WYSIWYG equivalent for programs?
Can WYSIWYG be applied to programming
?Several methods meet the goal of a more intuitive visual representation of the program.
IDEs use visual tools to create interfaces from assembled components that automatically generate source code.
UML (Unified Modeling Language), as the name suggests, is another way to model programs and move from visual presentation to compiled code.
But the oldest view is a sequence number, or organization chart. It can be upgraded using the object schema and their interaction through the messages they send, as shown below.
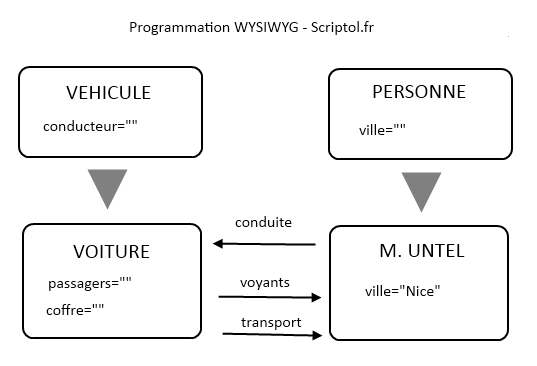
It can include object method sequence numbers.
An ideal, unencrypted representation of the program would be to display the application while it is running. So developing the program interactively at the same time as it works.
This is what can be done with LightTable EDI, which has a built-in rendering engine (Chromium) and allows you to edit a program while it is running, while seeing the changes displayed, without having to recharge anything.
See also...
- List of editors offline or online. Creating web pages in WYSIWYG mode.
- How to use Tiny MCE to edit static pages online.