Sitemap and Website Map Generator
The site map is appreciated by search engine robots in the XML version and users in the HTML version in order to navigate the site if necessary.
Currently, the sitemap is expanded with image and video tags, and even with a set of tags that make it the equivalent of an RSS stream.
You can create a site map with just one command with the script provided here, and edit the created document from the built-in viewer (or any text or XML editor), and then upload the file directly to the root of your site.
You must also save the file in XML or text format. The XML format used is a standard created by Google and adopted by Yahoo and Live Search (Microsoft).
- Concepts
- How to create a site map?
- Why make a site map?
- XML, text, HTML, which format to choose?
- Sitemap formats.
- Site Index.
- Multiple content on the same site.
- Things, important tips for site maps.
- Check sitemap.xml file
- Send Site Map.
- Generator sitemap.
- Resources.
Concepts
How do I create a site map?
Using the graphical interface, just specify the name of the home page and click the "Generate" button.
Why make a site map
?Whether in XML format and saved in Google or HTML, the map allows you to better link to a website. In addition, Google provides link analysis with a report of problems when saving the sitemap.xml file, as well as statistics.
It lists search results and pages that could not be indexed.
|
Simple map, screen
|
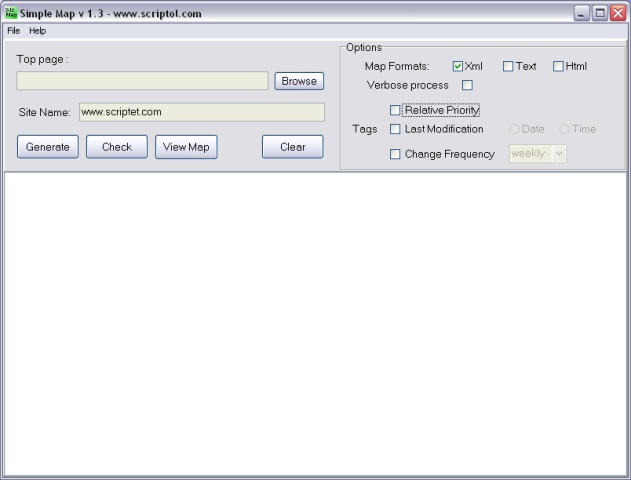 |
XML, text, HTML, which format to choose?
The XML format is now recognized by leading search engines. He gives directions to Googlebot and other search robots. This XML document is created by a simple map according to the format originally specified by Google.
- The priority tag indicates which pages are most important.
- lastmod tag - Specifies the last modified date that is used in conjunction with the frequency.
- changefreq tag - shows how often the robot should split the page, some always for a very large site and frequently changing pages to yearly or never for static documents (for example, official format specifications with version number).
The text format provides only a list of page URLs. It is accepted by Google.
The HTML format is intended for visitors to your site. He can view links, headings, descriptions and other information. It can only list part of the pages.
It is managed by search engines and can be used to indicate non-indexed pages to them, especially if there are several levels of directories, and the deepest ones are not always taken into account.
A text file or HTML is a simple URL list, but the XML format consists of tags that follow a standard format.
Sitemap formats
XML format
The container has urlset and contains a number of url tags corresponding to the pages of the site.
<urlset xmlns="https://www.sitemaps.org/index.htmlschemas/sitemap/0.9">
<url>
<loc>https://www.iqlevsha.ru/</loc>
<lastmod>2005-01-01</lastmod>
<changefreq>monthly</changefreq>
<priority>0.8</priority>
</url>
</urlset>Images in sitemaps
To index an image, use the following format:
<url>
<loc>http://example.com/sample.html</loc>
<image:image>
<image:loc>http://example.com/image.jpg</image:loc>
</image:image>
</url>Learn more about the Google Webmaster Center.
Video in sitemaps
See FAQs about video sitemaps, Google. (English)
Sitemap news
In addition to a URL containing a unique ID, a specific sitemap is required to post your articles to Google News.
This is a standard XML map with added tags.
In fact, these tags turn sitemap into an RSS file:
- <publication> is equivalent to a channel. It includes the tag "name" and "language."
- <access> with the value "publish," "free access" or "registration" is restricted.
- <genre> is optionally used to qualify the article type.
- <publication_date>, date and time of publication.
- <title>, article title.
- <keywords> optional.
- plus sitemap tags for URL, weight...
The sitemap should only contain articles published in the last two days.
sitemap index
An index is a file containing a list of sitemaps. It allows, if you have several sitemaps or the site map is divided into several files, specify their URL.
There is no need to create an index for one sitemap, and even sitemaps of different contents can now be combined into one, as we will see.
The index file is also in standard XML format.
The sitemapindex container and contains a number of sitemap tags.
<sitemapindex xmlns="https://www.sitemaps.org/index.htmlschemas/sitemap/0.9">
<sitemap>
<loc>http://www.example.com/sitemap1.xml</loc>
<lastmod>2004-10-01T18:23:17+00:00</lastmod>
</sitemap>
</sitemapindex>Multiple content on the same site
To cope with the multiplication of sitemap file types, Google decided to integrate all content types into one file.
A file with multiple contents looks like this:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<urlset xmlns="https://www.sitemaps.org/index.htmlschemas/sitemap/0.9"
xmlns="https://www.sitemaps.org/index.htmlschemas/sitemap-image/1.1"
xmlns="https://www.sitemaps.org/index.htmlschemas/sitemap-video/1.1">
<url>
<loc>http://www.example.com/mapage.html</loc>
<image:image>
<image:loc>http://example.com/image.jpg</image:loc>
</image:image>
<video:video>
<video:content_loc>http://www.example.fr/mavideo.flv</video:content_loc>
<video:title>Regardez grandir le petit dernier.</video:title>
</video>
</url>
</urlset>So, three types of tags in the URL tag: loc for the page, image and image: loc for the image file, and video from the video:content_loc..
Important tips for website maps
XML Site Map
- The XML format is recognized by at least Google, Yahoo and Bing.
- XML sitemaps are necessary if you use dynamic links to your articles (link in JavaScript).
- If some pages are not already indexed, they should have a higher priority with the priority element of the XML file.
- To remove a page from indexing by search engines, you must use the Robots.txt file or the "ROBOTS" meta tag.
- Map for the entire site. Do not create a map only with pages that are not yet indexed by Google.
- Time variant ("Time") - for giant sites! One date is enough in most cases.
- Sitemap, whose pages all have the same maximum priority and read rate, is the highest, has zero interest in Google. Give pages the lowest priority and frequency if they are already indexed and unchanged.
- A tag has been added to the sitemap protocol for the video. See Google's sitemap video tutorial.
Video beacons are placed in a separate map .
HTML site map
- You can create an HTML sitemap for visitors and XML for search engines.
- Place a link on the HTML site map on the home page.
- When a page is added to a site, it is not indexed for several weeks. Despite the fact that search robots scan the site daily, the database is updated for a set of sites between weeks or months.
RSS Site Map
- The RSS file is a valid site map for Google, but only for recently added pages.
sitemap index
- The index can contain URLs of 50,000 sitemaps, each of which can contain 50,000 URLs of web pages.
Check sitemap.xml file
This is the address of the site that will validate your sitemap XML file. You need files:- sitemap.xsd, format scheme, included in archive.
- sitemap.xml, a list of pages on your website or local computer.
See resources.
Send sitemap.xml sitemap
The XML file must be placed at the root of the site, such as index.html or index.php.
In sitemaps.org opinion, an xml file can be sent in three ways:
- Save the map to the search engine website.
- Add line to robots.txt.
- Query the server using a script or browser.
Add a card
Create an account in Google Webmaster if you don't already have one.
Google will provide you with an identification file to download to your site, and after that you will still return to your Google account and click the "Verify..." button. Then forget about them the day before you return to your account for results.
Ping
You can also save the map via ping, see "What is I do after I create my Sitemap?" in the FAQ mentioned below in the resources.
When your sitemap is updated, you should not register it again, you can tell the search engine via ping:
https://www.google.com/ping?sitemap=http://www.example.com/sitemap.xmlReplace iqlevsha.ru with the URL of your site, and google.com with the corresponding search engine domain: yahoo, ask, etc.
Use robots.txt
According to the Google blog, you can now add an entry to the robots.txt file for the site map, and it will be euthanized when Google robots and other search engines meet with these files.
The syntax is as follows:
User-Agent:*
Disallow:
Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xmlThe robots.txt file is placed at the root of the site, for example, the sitemap file and the index.html home page, or another.
You can, if you have several sites, give in the robots.txt file one site, the URL of the sitemaps of each site, one per line. Link.
User-Agent:*
Disallow:
Sitemap: http://www.example.fr/sitemap.xml
Sitemap: http://www.example.com/sitemap.xmlSitemap Generator
How does it work
The program recursively maps the content of the site, starting from the home page, to each page associated with it and builds a list of all pages that will be referenced by search engines.
A valid list of extensions in the source code determines the type of files to undo.
The program is currently running on a local site image. There are a number of sites that offer to build a site map directly on the hosting site.
Syntax:
php smap.php [options] site-url dépôt-local
Example:
php smap.php http://www.example.com c:\example.com
To view parameters, enter:
php smap.php
A list of recognized extensions and files to exclude is in the options.php file. You can automatically exclude files with a label:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">
Shape
You can adapt the program to your site by changing the variables in the options.php file (or option.sol for the source).
- Site map name. You can also change it in smap.ini.
- List of valid extensions.
- List of files to exclude.
- List of directories to exclude. You can exclude only files from the directory, not subdirectories with an asterisk.
By default, the program can work with static WordPress files. Then add the content to the dynamic node map.
Get the program
- Download the latest version of the simple card with
- Download version 1.4 executables and GUI.
See old version manual (English).
Get source code
The command line script source is included in the archive. This is a Script program, it is clear and compact thanks to the text processing functions of this programming language.
License from Simple Map: Mozilla 1.1.
Changes
- 2.0 - October 13, 2016
The program for building a map from a single directory content has been completely rewritten. Requires a list of files to exclude (or unrecognized meta-robots or extensions). - 1.7 - July 1, 2015
Suitable for Script 2 compiler. - 1.6 - 13 July 2009
Fixed PHP 5 compatibility issue in addLink for smap.sol.
The binary version of the software has not changed. - 1.5 - March 14, 2008
The program now runs on the command line with PHP 5.
The issue with capital letters in Linux has been fixed.
The algorithm is completely rewritten, the source is easier to read and, if necessary, edit.
The binary has not been modified for this version. - 1.4 - May 2007
The interface does not change, it is still version 1.3, but the command line program used is rewritten.
Now the meta tag "robots" is taken into account when eliminating pages in "noindex" or "none."
The algorithm has been rewritten to better handle subdirectories.
The source code can be compiled with the latest version of the compiler. - 1.3 - August 2006
The smap.log file is sometimes not found. This has been corrected. - 1.2 - February 24, 2006
Now you can generate several types of cards at once.
Better handling of links containing Internet Protocol. - 1.1 - 23 February 2006
Tags with a blank value are no longer added to items. - 1.0 - February 22, 2006
Initial distribution.
Resources
- Sitemaps.org - Official site common to Google and Bing with full specification.
- Robotstxt.org. Learn more about robots.txt.