WebRTC vs WebSocket
Two ways to communicate with the server, what do they represent and what is the difference?
WebRTC wants to allow real-time communication between the browser and the server and between browsers. RTC stands for Real-Time Communication. The web API that allows it to be used in the application is an object of the W3C standard, which describes the interface of objects involved in such communication.
It is clear that Microsoft wants to invest in this kind of technology (based on its recruiting) and that it will be integrated into Skype, a free computer telephony service, as in the case of Google Talk. Microsoft did not implement WebRTC on the pretext that the VP8 code it uses may include patents. A recent agreement (March 2013) with MPEG-LA that withholds them clears that hurdle.
WebRTC is supported by Google and therefore uses the VP8 codec for video. Google is asking for this codec to become the standard for WebRTC, and for the Opus codec to be sound. Both without patents. They are already used by Skype, among other codecs.
In November 2014, the RTCWEB working group decided that both VP8 and H264 are mandatory in WebRTC. Therefore, browsers will have to implement both codecs .
Difference with WebSocket
WebSocket, which is also defined by the IETF and W3C, is a two-way communication protocol between the server and the browser. The W3C standard describes the API for its use in an application. WebRTC is a two-way real-time protocol for images and sound between browsers or servers.
In both cases, you have an interface that can be used in JavaScript by webmasters, and an internal communication protocol that is used by browser authors. The second protocol may be used first.
WebRTC actually describes two APIs, one of which is the web API, which is described in the W3C standard, is all that interests webmasters. Another API in C++ that allows you to connect to back-end multimedia services is used by the creators of browsers and other software.
Here is a diagram of the various levels of the WebRTC interface:
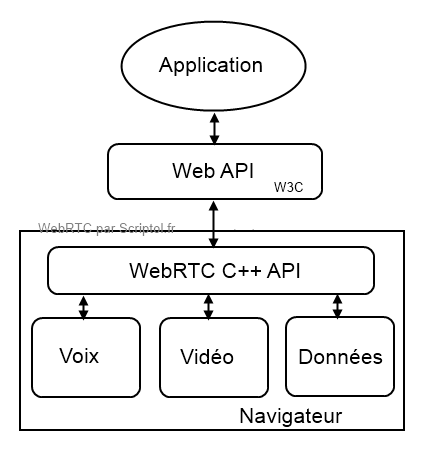
The WebRTC web API is a replacement for Ajax as WebSocket replaces the browser's XMLHttpRequest object. However, we are at a completely different level with real-time two-way access, without waiting for the server. The system needs to withstand this load, so it is designed to run the application on a dedicated server. But the ability to distribute remote browsers opens up new horizons for app creators.
RTC Object
In October 2014, Microsoft announced that Internet Explorer would support ORTC. It is an extended JavaScript API based on RTC. For Microsoft, this was a difficult decision, since allowing browsers to communicate voice and visually makes services such as Skype useless (it bought it in 2011 for $8.5 billion), or at least makes it easier to create competitors, but it was necessary in order to stay at the level of Firefox and Chrome.
Documents and code
- WebSocket vs. XMLHttpRequest.
- Ortz knot. Implementation of the API in Node.js, therefore, for exchanging local or local stations with the browser .