XML - Extensible and Universal Data Format
XML, "eXtended Markup Language" is a successor to SGML, like HTML, but more general, it includes data in the names of the tags themselves and therefore has unlimited descriptive capabilities.
The display format is independent and depends on the associated structure, XSLT. Tags are created and validated according to the rules specified by the DTD (Data type dictionary) describing the grammar (tags), or Schema, another validation tool written in XML itself .
XML, like HTML, is processed by many programming languages, and especially JavaScript, through the DOM (Model Object Document) interface. The document is fully loaded into memory, and its structure is stored for access to any tag or set of tags using internal search procedures.
For larger documents, SAX mode is used instead, in which case the XML in the file is row-wise and each tag is processed after being loaded into memory.
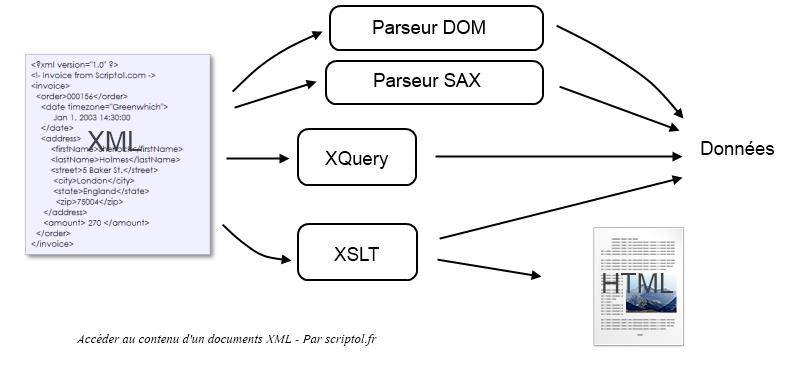
XML is characterized by significant tags created from document data. The role of tags depends on their content and the tool that maps the XML document. The name of the tags is selected for readability of the document, their role depends entirely on the tools that will access it.
Example code, save invoice in XML:
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<!- facture de Corp. ->
<facture>
<commande>000156</order>
<date timezone="Greenwhich">
Jan 1, 2003 14:30:00
</date>
<addresse>
<nom>Sherlock</nom>
<prenom>Holmes</prenom>
<rue>5 Baker St.</rue>
<ville>London</ville>
<pays>England</pays>
<code>75004</code>
</addresse>
<montant> 270 </montant>
</commande>
</facture>A related presentation and validation document is required. Browsers recognize multiple doctrines that describe a single version of XHTML or HTML code, and are able to handle the CSS presentation language for each version .
Outside Text Document
XML is never just semantics, a language with elementary syntax that the tool can "speak," that is, turn words into actions. It is not only used for text content.
Let's start by looking at several applications from the SVG language. They are amazing, they make vector graphics that can even be revived. However, SVG is nothing more than a subset of XML to which we associate an API. Tags become rectangles or different shapes, and their attributes change to produce animation. SVG is a browser-friendly language (or SVG renderer) for representing images of variable size.
Another example is the RSS format. Once a role is assigned to each tag, the list of links and descriptions becomes a press magazine.
In the XHTML dialect, each tag has a formatting role. It is a subset of XML, semantically equivalent to HTML, that tells browsers how to present their multimedia content.
XML or JSON
?Web pages could also be expressed in JSON files, which would reduce the size of the files, but probably slow down the development of web pages, as HTML code remains significantly more accessible to non-programmers .
For the application, the choice of format is disclosed in the article JSON or XML, which format to choose? But do you really have to choose? These are two ways of presenting the same thing: structured content and converting one format to another is not difficult. In fact, once content is loaded into memory and translated into objects and attributes, serializing it as an XML file or JSON is simply a matter of personal convenience.
Therefore, the main goal of the article is to decide when a particular format is better suited for storing data, depending on the language or system in which they are used.
XML Tools
You can use multiple tool classes to access contained data, edit a document, or convert a document to another format.
Parsers
There are two types of parsers. The tree parser loads the entire XML document into memory, and the content can be accessed using the Document Object Model, in particular using statements such as getElementsByTagName.
In contrast, under the SAX API, the event substitute gradually loads the content and stores either all the data or those requested.
- Pugixml. A lightweight and very fast tool written in C++ and integrated into the program as a source or binary file.
- Xers. The Apache website provides a Java or C++ (Xerces) XML parser, as well as several other XML tools. It uses DOM or SAX APIs.
- LibXML. C library using DOM or SAX API.
- Expat. Library for building an evenmental parser (used by Scriptol and XCheck).
JavaScript + Node + HTML does not require an XML parser. This is built into the browser. Therefore, such parsers are only useful for C++, Java, or other languages.
If you just want to check if the XML is formed correctly, download XCheck for Windows here.
XQuery
XQuery is an XML database query language, be it a file or a database with a tree structure similar to XML, like Apache's XIndice.
Thus, it allows you to create an XML database and use it. Download the GNU implementation.
XSLT
The XSL language consists of translation rules. XSLT converts an XML document to another format, such as HTML, and can be used to access data. Xalan, converts an XML document to HTML. Exists in Java and C++.
Publishers
Doctor of Science. A simplified editor for XML and DocBook 5 that represents code without parentheses. Multiple schemes. Open source on GitHub.
Virtual machine
Xmlvm is a kind of bytecode in XML. It can be compiled in Objective C, JavaScript, bytecode Java.