Latent Provisioning (LDA) and Google
Studying the LDA algorithm (Dirichlet latent extraction) is a new trend among webmasters. It raises some of the secrecy of Google's search engine algorithm and partly explains how links on results pages are selected.
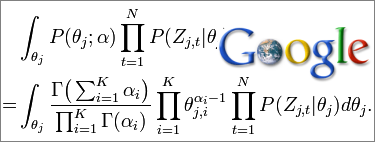
This trend was initiated by Seomoz.org site when it proposed a web page rating tool using this algorithm. This tool gives an assessment of relevance in relation to the query, the more relevant it is and the better it is assumed that it will appear in the results of search engines.
The validity of the assessment was tested experimentally.
The word Dirichlet comes from Johann Peter Gustav Lejeune Dirichlet, a German mathematician who studied in France and joined French mathematicians of the 19th century, who was engaged in work in the field of complex analysis and probability laws.
The LDA algorithm was first described by David Bley in 2003, who published a paper hosted at Princeton University: Latent Dirichlet Relation.
The paper "Online Inference of Topics with Latent Diirichlet Assistance," published by the University of Berkeley in 2008, compares the relative advantages of the two LDA algorithms.
What is LDA?
LDA has the most important purpose of ranking, it allows you to associate a context with a document from the words contained in this document, which can relate to different contexts .
For example, the word "robot" can mean a program (search engine robot), or a machine (android robot). Analysis of words close to this word on the page allows you to determine whether it is a page or paragraph about programs or machines.
Search engines determine the context based on the request and habits of the Internet user, previously visited pages. Then they have to find pages containing query keywords, but in the context of the Internet user and LDA, then it is applied to pages in the index.
The algorithm is a Bayesian model, so it aims to determine the probability of the hypothesis. Since it is about linking a keyword or group to a context, a hypothesis is a context, and there are several competing ones.
Also in computer science, Bayesian conclusions are used and bots are trained, for example, to create a spam filter .
Using a search engine algorithm may be more efficient than using a predetermined code.
Quote (Griffiths and Staver):
Latent Diirichlet Relation (Blei et al, 2003) is a powerful learning algorithm that allows you to automatically and jointly classify words in contexts and documents in a mixture of contexts. It has been successfully applied to model changes in scientific fields over time .
LDA and Optimization
Seomoz created its tool by finding a correlation of Google results with this algorithm. The takeaway is that Google is integrating LDA into its algorithm, which is broader and includes many other criteria.
LDA is mainly content based. Google's algorithm contains criteria not only for content, but also for the number of links per page.
Experience shows that the first links on Google's results pages have more relevant content than those that come after.
For optimal use of this algorithm, it is best to strengthen the page context over the query to be answered by adding words related to keywords already associated with that query.
But you need to avoid some pitfalls...
What's not LDA:
- This is not a criterion for keyword density.
It is useless to accumulate the same keywords in the hope of seeing a page better located on the result type. It is used only to find the context of the page and for this it is important to choose words, not numbers. - It's not a dictionary of synonyms .
Associations between words representing different but related things are important. It is also useless to accumulate synonymous words, at least compared to LDA, because it can be useful more generally.
Repeating a keyword does nothing, but repeating the context the other way around can be helpful. Keyword groups related to a topic, such as programs or machines, that appear multiple times on a page can improve its positioning.
Documents and code
- Implementation of LDA on Hadoop by Yahoo! Code on GitHub .