Panda Open Patent
Simplified description of patent 8,682,892 for ranking pages, images and other resources, suggesting punishment for low quality content.
Three years later, Panda's algorithm was introduced, declassifying tens of millions of websites (roughly 20% of 300 million), questioning the business of webmasters, and bankrupting countless e-commerce sites. We will be happy to know that the famous algorithm that should judge the quality of websites and "create a healthy ecosystem," according to Google, boils down to a simple equation: M = IL/RQ!
However, in the study of patent 8.682.892, there is no doubt that the positioning method, the effect of which is fully consistent with the new work of the search engine, which began on February 24, 2011...
- That benefited major sites like Amazon, eBay, which saw its traffic grow 30%.
- This affected mainly the middle sections. Many e-commerce sites have closed their doors. And
- benefits brand sites.
- Sites are affected entirely, not just pages of less interest.
- Old sites suffered more than new ones.
- Affected sites almost never restore an audience, even if they improve their content. Some, however, were able to recover by deleting most of their pages.
- 12% of sites suffered from the first iteration and even more so from subsequent .
- Panda requires huge resources, and first of all it is implemented through an independent program, which is launched about every month. We now know that this is to build the resource group partitions of all websites.
- This was presented by Google as a way to lower the quality of pages. This is the goal set in the patent.
Then Google considered this method worthy of a patent and on September 28, 2012 filed specification 8.682.892.
And this method is in detail...
Panda method
The process used to change the ranking according to the Panda factor is to divide the index into groups of resources that are considered related to each other.
1) Resource groups are defined
The entire website is divided into resource groups. Resources are pages, images, and other documents that can appear in the results and are in the index.
Resources are classified into one group based on their URLs, and the group includes all domain, subdomain, domain set, or single hosting documents.
Google can also determine group affiliation based on common elements: the same presentation, the same stylesheet... (It is hoped that he will not assimilate into the group all sites that use Bootstrap!).
Once a group (site or node set) is defined, it is assigned a Panda factor to be applied to each page of the group. Below we will show how this factor is calculated.
To simplify the description, a group of resources will be designated as a "site" and a resource as a "page," but you think it is more difficult .
2) The starting score of the page is determined.
When the system receives a request from the user, it also receives a list of pages with an initial score for each of them .
This one was previously calculated by a conventional algorithm using 200 criteria, including PageRank.
We have to change it with the Panda factor.
3) We identify the group...
For each page, the program determines the site to which it belongs based on its URL. Knowing the site, he restores the Panda factor associated with it.
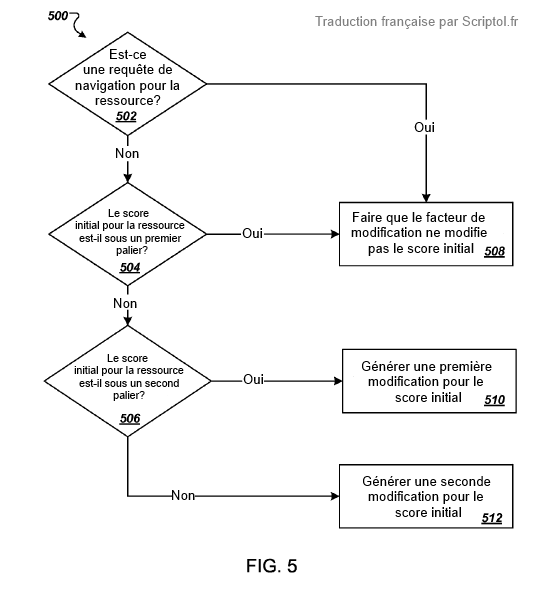
4) Creates a page-specific factor
Something more specific is calculated from the Panda factor of the site. To do this, compare the initial page score with two consecutive levels.
If the initial score is below the first level, the Panda factor is cancelled.
If the initial score is between the first level and the second level above, a specific factor is calculated that falls further as the initial score increases.
If the initial score is above this second level, the Panda factor in the group is changed by a formula or algorithm mitigating its effect.
5) Navigation queries are excluded
When a user makes a query aimed at finding a specific site or page, specifying a domain name or terms specific to the site or page, the Panda factor is ignored and the page will be classified by its initial score.
6) The change factor is applied to the initial estimate
The Panda factor is multiplied by the initial score to get a new rating score and the latter will be used to classify the resource in the results.
Calculation of change factor
This is how the Panda factor is defined for a group of resources, that is, an associated site or set of nodes.
1) Breaks the index into resource groups
This is based not only on URL, but also on other factors to determine the same owner for a set of resources. A group is defined as a domain or subdomain, or set of domains belonging to the same person or organization.
2) The number of independent links to the pages of each site is calculated
Not only explicit links to a site are considered, but also links to it, for example, a domain name even without a link tag. Links are independent if they do not belong to the same resource group, so, depending on the case, they belong to the same domain, subdomain or nodes of the same owner, or multiple nodes connected to each other.
But you can also try to find a link between the source and target pages. Same stylesheet, similar content, same frames. One can calculate the independence value and estimate that this value is too small to infer the independence of the link.
The system stores only the link on each page of the source site.
It adds up all the independent connections .
3) The number of requests for site pages is calculated
The number of reference requests per node/group is calculated. These are requests made by different users to the pages of the site. Users are identified by IP, cookie, or any other method.
Add up all the help queries.
4) Ratio determined to obtain Panda factor
Facteur de modification = nombre de liens indépendants / nombre de requêtes de référence.
5) Normalise the Panda factor
In some implementations, the coefficient of change is normalized .
The intervals of the number of help requests are determined and the index is divided into a set of nodes/groups belonging to the same interval.
Each site's Panda coefficient is normalized based on other sites in the same section, i.e. from the same interval.
To do this, the average or median or other such measurement is calculated and the formula is used:
Facteur de modification normalisé = facteur de modification - mesure / mesure.
This new value is saved instead of the initial change factor.
Subsequent changes
Panda has received several changes, some of which have been made public...
Niches. Some sites provide unique information in specific sectors and yet have very few inbound links. We tried to fix Panda to save these sites.
Matt Cutts also said that in the new iteration, Panda took into account the fact that when users registered on a Google account often exclude a site from the results pages, it receives a reduced score.
On May 20, 2014, a major update allowed many small sites to exit the Panda sandbox. Despite the fact that the nature of the change in the algorithm was not disclosed, it is clear that Google eventually took into account that a small site cannot have as many backlinks as an important one. Thus, he responds to the criticism formulated in conclusion .
Algorithm and its effects
By facilitating return links, Panda promotes new and relevant pages, hype. The backlinks accumulated by old sites disappear over time...
Panda does not remove stupidity from the results pages, such as "if you are looking for a screw that does not break, buy in a stronger one." But such an answer is now given by large general sites that take the place of content farms. A new trend ?
SEO is losing a lot of interest in Panda. No amount of reference work can increase the number of fully independent feedbacks. They depend on the content. And activism. But knowledge of searchers is still useful for solving many webmaster problems, such as redirects, domain changes, duplicates, microdates, etc.
With equal quality, the more visitors the site has, the more likely it is to get backlinks. The ratio explains why the site can't recover after being fined by Panda: how do you get more links to returns when the audience has shrunk significantly?
Knowing that one site receives 10,000 visitors daily, and another - 1000. If they each put a page on the same topic with the same keywords and get the same initial score, then the former will have ten times more links due to the number of visitors and therefore a better Panda factor.
But how does this indicate a higher quality of content?
When the answer to a difficult question does not appear on an important site, it becomes more difficult to find it. Popularity is privileged .
Depending on the ratio used, if a site presents an image that goes viral and receives a million links, anything published on that site will be considered quality and receive a better rating. The quality of sites according to the concept of Google is assessed according to a low quality algorithm.
Update May 2014: During a new iteration on May 20, it seems to have been taken into account (after 3 years) that a smaller site cannot get as many backlinks even with original and informative content.
By Denis Suro, 14 April 2014.
Other images accompanying the patent:
- Search engine scheme. On which the patented method is implemented.
- Panda algorithm steps.
- Calculates the change factor.
- Normalization of the change factor.