What you need to know about PageRank
Google PageRank is part of an algorithm and index that measures the popularity and value of a page on the web. This is one of the main indexes for ranking search results .
A legend circulated by webmasters with a very partial understanding of search engines claims that "Le PageRank is dead."
It is not and never will be. Of course, innovative search engines like Wolfram Alpha have a completely different and promising approach, but in addition to accounting for a negligible share of web searches, they provide the content pages they produce, rather than lists of external pages, and therefore should not deal with spam. PageRank will always be important for estimating the cost of a page.
- PageRank is a registered trademark.
Initially, this is a pun on the word page and the name of one of the two founders of Google, Larry Page . - Google's success stemmed from its use of the PageRank algorithm.
It classifies sites by links, not by the number of keywords on the page, as the AltaVista search engine did (few Internet users still know AltaVista). - PageRank helps position the page in Google results.
But that's a clue among many others.
See Google's patent for evaluating pages. - PageRank is an index proportional to the number and importance of links on the page.
It depends not only on the number of backlinks: PR pages are the most important factor.
(Ref: The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine). - PageRank affects indexing, pages are cropped in descending order of PageRank.
The pages that have the highest PR are scanned most often and most completely. There will also be linked pages, but the more links, the less control.
(Reference. Matt Cutts). - The PR of the page passed to the linked pages is divided by the number of links.
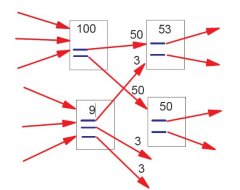
The value passed generally corresponds to the PR of the page divided by the number of links per page, as shown in the graph to the right, whether follow or nofollow .
(Ref: The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine). - The nofollow attribute in the reference does not pass PR to the page that is linked .
But his share of undivided PR is not redistributed to other connections, it is lost.
See PageRank and nofollow.. - Increasing the PageRank score has a gradual complexity.
It does not depend linearly on the importance of backlinks, but logarithmically. Thus, with constant progress, we will need much longer to increase from 4 to 5 than from 3 to 4. - Multiple links on the same page matter no more than one.
One page transmits to each other no more PR with several links than with one. Only the first is taken into account, in addition, if the anchors are different, then the binding of the first link is taken into account when assigning keywords to the target. - All pages are equal.
The algorithm does not highlight the index page or pages at the root of the site and pages in depth. He highlights Landing Pages, the ones that are popular and have the most backlinks, and others. Popular pages transmit PR and traffic to others. Depending on this, you need to study internal relationships. - PR can be conveyed by links in images.
That's Google's claim. - 301 Redirect Loses Part of PageRank
PageRank is not completely transferred to a new page when the page is redirected by redirection 301. As a result, it may lose positioning in SERPs. This was confirmed by Matt Cutts and tested experimentally. - Changing page content can change the weight of backlinks
Links indicate the exact content. If the page changes, it must have new links to keep its PR. Changing the content of a page after it has become popular is a spammer technique, so it can cause a fine in addition to losing PR. - Plagiarism can gain an advantage over the original thanks to PR
When two pages are identical and the indexing date is not enough to determine which is the original and which is the copy, Google believes that the one with the highest PR is the original. This was clearly stated during an interview with Matt Cutts by Stefan Spencer.
In addition, a Google blog article explains the negative impact due to a duplicate satisfied. - Google tried an algorithm that does not take into account backlinks
Matt Cutts explained it in the video. The results are much worse in terms of relevance than the algo results that take them into account, so the experiment did not leave the laboratory. - Companies claim to guarantee PR against payment
But Google claims: no one can guarantee PR, whatever it is. Therefore, it is useless to hope for miracles. If you do not understand anything about sending, you can always contact the company that undertakes to do the work for you, for a reasonable fee, without promising formidable results. You can always improve positioning when the site is initially poorly designed and no background work has been done. In - In 2016, Google stopped making the PageRank index publicly available. It has not been updated since 2014. The indicator has already disappeared from Google Webmaster Tools since 2009.
Links: SEO for bloggers, Author: Matt Cutts (English), The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hyertextual Web Search Engine from the founders of Google .