Search Engine Anatomy: Google Infrastructure
The design is based on a description provided by Google founders Lawrence Page and Sergey Brin.
Since 1998, this document has been simplified, and in particular, the PageRank module must be designed in several units, taking into account various criteria, including user behavior.
Search Engine Architecture
(c) 2010 .com/.fr - No reuse on web page
Components
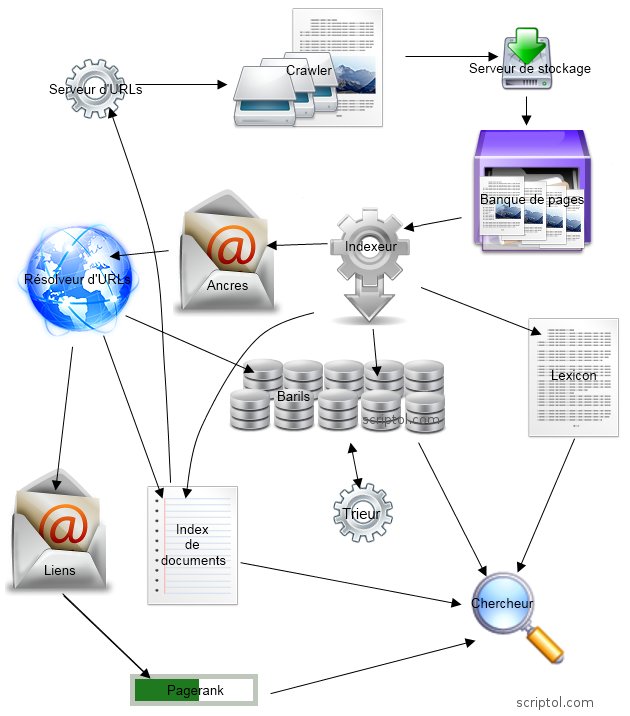
| Crawlers | There are several of them, they distribute them, they say pages, find links and keywords in them . |
| URL Server | Contains a list of URLs to scan. |
| Bank server | Crowler sends the collected data to the bank's server. It compresses the pages and places them in this view in the vault. Each saved page has an ID, docID. |
| Bank | Contains a copy of pages and images, allows comparisons and caching. |
| Indexer | It indexes pages to provide their SERPs (results). It unpacks documents and converts them into a set of words called "hits." He hands out hits among the barrel ensemble. This gives a partially sorted index. It also creates a list of URLs on the page. Hit contains the following information: word, its position in the document, font size, capitalization. |
| Barrels | These figurative barrels are databases that classify documents by docID. They are created by the indexer and used by the sorter. |
| Anchors | The reference file created by the indexer contains internal references and the text associated with each reference. |
| URL solver | It contains the contents of the binding file, converts relative URLs to absolute addresses, and finds or creates a docID. It creates a document index and a relationship database. |
| Document Index | It contains text for each URL. |
| Communications | The database of links associates each of them with a docID (therefore, also with a document on the Internet). |
| PageRank | The program uses a reference base to determine the PageRank of each page. |
| Sorter | It interacts with barrels. It plays documents classified by docID and creates a reverse list classified by wordID. |
| Lexicon | Software called DumpLexicon takes the list provided by the sorter (classified wordID) and also repeats the lexicon created by the indexer (list of keywords on each page) and produces a new lexicon for the researcher. |
| Researcher | It runs on a web server in a data center, uses a lexicon produced by DumpLexicon in conjunction with an index classified by wordID, accounts for PageRank, and creates a results page. |
It goes without saying that this scheme is simplified. The system tends to become increasingly complex with added time and features.
Links
Anatomy of a wide scale hypertextual web search engine. Larry Page and Sergey Brin.
This document in English, posted by Stanford, probably dates back to 1998 and describes in detail the operation of the search engine. This document is his resume and contains the new .com/.fr.
How search works
The explanation of the Google search engine is very developed. (English).
Icons are either created for Script or taken from a bank of free-use icons.